Single Arm vs Double Arm Street Light Bracket Differences
When you plan a road lighting project, you might focus entirely on the brightness of the bulbs, but the physical hardware is just as vital. The poles, arms, and brackets you select form the lighting support system that determines whether your lights actually do their job. If you pick the wrong components, even the most expensive lamp will fail to provide the right coverage, leading to dark spots and dangerous glare. You must treat these structural elements as the foundation of your system because they dictate exactly where the light lands and how well it covers the pavement.
Structural stability is a major factor in how long your setup lasts and how safe it remains for the public. A pole that cannot handle wind or a bracket that lacks the strength to hold a heavy fixture creates a serious risk. Beyond durability, your hardware choices affect installation safety and the ease of future repairs. Planners look at these components to ensure the light is positioned at the perfect height and angle to help drivers see clearly. By choosing high-quality hardware that matches your specific road needs, you improve the load distribution and the lifespan of the system, making the streets much safer for everyone who uses them.
What role do poles, arms, and brackets play in street lighting systems
Street light poles, arms, and brackets act as the structural framework that positions the light source. The pole provides the necessary elevation, the arm extends the fixture over the roadway for optimal fixture positioning, and the bracket secures the lamp, allowing for precise load transfer and alignment control.
Poles are the backbone of your system, acting as the primary structural support that keeps your fixtures at the right elevation. Without a sturdy pole, the light source cannot maintain its position against wind or vibration. While the pole provides vertical lift, the arms are responsible for reaching out over the pavement. This ensures the light is centered where it is needed most, rather than being wasted on the sidewalk. Brackets serve as the critical connection point, managing the weight and ensuring the fixture doesn’t shift over time. If any of these parts are mismatched, the entire system loses its effectiveness, leading to poor visibility and potential safety hazards.
How do different street light pole shapes affect performance and use
Pole shapes, or pole geometry, dictate the structural strength and wind resistance of the unit. Tapered poles offer superior load distribution and vibration dampening compared to straight poles, while multi-sided polygon poles are engineered for the extreme structural rigidity required in highway or stadium environments.
The shape you choose significantly influences how the pole behaves in various environments. Straight poles are consistent in diameter, offering a classic look often used in parks or low-speed residential areas. However, tapered poles—which are wider at the base—are generally superior for high-stress environments. The tapered design allows for better weight distribution, making the pole more resilient against the constant vibrations of passing heavy traffic. Planners must weigh the application suitability of these shapes against the specific needs of the project to balance visual appeal with the physical endurance required for long-term road use.

Why pole height is critical for light coverage and safety
The pole height determines the total coverage area and the uniformity of light on the ground. Correct mounting heights prevent the creation of “hot spots” and deep shadows, ensuring visual comfort and allowing drivers to spot obstacles from a safe distance without experiencing blinding glare.
Selecting the correct height is one of the most impactful decisions you will make. As you move the light higher, the beam spreads further, allowing for a more uniform glow across the pavement. If your poles are too short, the light is concentrated in small, intense pools. Conversely, on multi-lane highways, taller poles are necessary to push light across several lanes without requiring a dense forest of poles. Finding the “sweet spot” ensures that you maximize visibility while minimizing light pollution and spill into residential windows.
How do arms and brackets control light reach and positioning
Arms and brackets manage the light projection and final fixture alignment of the lamp. The arm length dictates how far the light extends over the driving lanes, while the bracket allows for specific tilt adjustments to manage glare and ensure the beam hits the target accurately.
The arm length you choose is your primary tool for managing light reach. On roads where poles must be set back from the curb, a longer arm is required to ensure the center of the road receives intense illumination. Brackets further refine this by allowing for specific tilt and rotation. This precision is what helps you avoid dark spots in the lighting layout. If a bracket is not designed to hold the light at the correct angle, the beam may cut off too early, wasting energy and reducing the effectiveness of the entire plan.
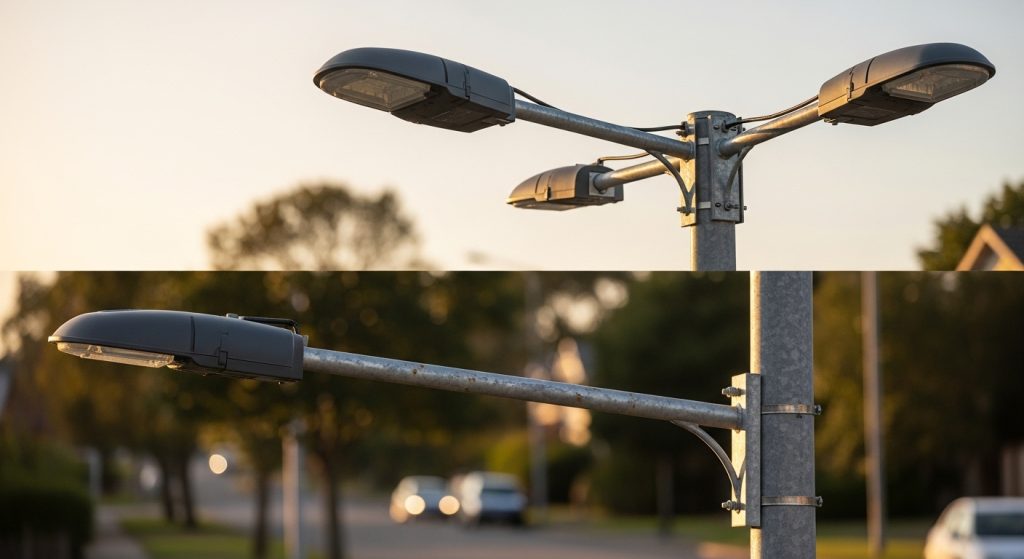
When should single or double arm configurations be used
A single arm configuration is ideal for standard roadside lighting on narrow to medium roads, while a double arm setup is preferred for central medians where dual illumination is required to light both directions of traffic from a single pole.
Choosing between these configurations depends heavily on the road width and your pole layout. Single-arm setups are cost-effective for standard two-lane roads. Double-arm configurations are typically utilized when poles are placed in a central median. This allows a single pole to light both sides of a divided highway. While this reduces the total number of poles needed, it significantly increases the load distribution requirements. You must ensure the pole is strong enough to balance the weight of two fixtures and resist the torque caused by wind hitting two different directions.
How do material choices impact pole strength and lifespan
The material strength of your poles, typically aluminum or steel, determines their service life and corrosion resistance. Steel provides the rigidity needed for high-load areas, while aluminum offers a lightweight, rust-proof alternative ideal for humid or coastal environments.
Steel is the most common choice for heavy-duty applications because of its immense durability and lower initial cost. However, it requires high-quality galvanization to survive in wet environments. Aluminum offers a lighter, modern alternative. While it may not have the raw strength of steel, its natural resistance to oxidation makes it an excellent choice for salty air. When you select a material, you are choosing the maintenance schedule for the next 30 years. Steel provides the muscle for high-wind areas, while aluminum provides longevity for corrosive environments.
Why wind load and foundation design cannot be ignored
Proper wind load calculations and foundation design are essential for structural safety. Every pole acts like a sail; without a deep enough base to handle the overturning moment, the leverage created by wind and height can cause the structure to fail.
Every street light pole catches the wind and transfers that force down to the ground. If you use a large fixture without accounting for the wind pressure, the pole can bend or snap during a storm. Foundation stability is equally critical because it is the anchor for the entire system. A pole is only as strong as the concrete base holding it. If the base is too shallow, the pole will lean over time, ruining your lighting alignment and creating a risk to public safety.
What mistakes lead to premature failure of poles and brackets
Common design mistakes include ignoring total structural load calculations, choosing incompatible arms for a specific pole shape, and poor maintenance planning. These errors lead to sagging, vibration damage, and localized rusting that compromises the system’s integrity.
Many failures happen during the planning phase. One frequent error is ignoring the total weight of the fixture when selecting a pole. If the pole isn’t rated for that load, it will suffer from metal fatigue. Additionally, poor installation planning—such as using the wrong fasteners—can lead to alignment issues where brackets aren’t leveled properly. Vibrations from wind and heavy trucks can slowly loosen hardware that isn’t secured correctly. Avoiding these blunders requires accurate weight calculations and ensuring that the installation follows a strict quality control process.
What should be reviewed before finalizing street light pole and arm selection
Planners must perform a final design validation by checking road width against arm reach, verifying wind ratings, and ensuring foundation adequacy. This selection checklist acts as the final safeguard to guarantee operational reliability and long-term project success.
- Confirm the pole height provides the right spread for the road classification.
- Verify the arm length provides enough overhang to reach the driving lanes.
- Check the wind load rating of the pole against local geographic weather data.
- Ensure the material (steel or aluminum) matches the local environmental corrosion risks.
- Review the bracket adjustability to confirm the light can be aimed precisely.
- Validate that the foundation design is sufficient for the total height and weight.
- Ensure the hardware allows for easy access during future maintenance cycles.
What are straight light poles and where are they commonly used
Straight light pole specs describe poles that maintain a uniform diameter. These straight poles are effective for urban roads and parking lots where aesthetic consistency is a priority. Because they lack the natural load-distributing properties of tapered designs, they are usually found in areas with lower speed limits and less intense wind exposure. They offer a clean vertical line that fits perfectly into modern cityscapes and pedestrian-friendly zones.
Why are polygon light poles preferred for highways
Polygon light pole highways are used in major infrastructure because their multi-sided shape provides superior resistance to bending. These polygon poles are specifically engineered for highway lighting where they must stand tall against the high-velocity air displaced by speeding trucks. The flat surfaces help the pole resist twisting forces better than a standard round pole, making them the most reliable choice for high-speed corridors.
What benefits do foldable light poles offer for maintenance and safety
Foldable light pole benefits focus on the ease of maintenance access. These poles can be lowered to ground level, which eliminates the need for bucket trucks and improves safety design. They are particularly useful in areas where a truck cannot easily reach, such as narrow park paths. By allowing hardware to be serviced at eye level, you reduce the risks associated with working at heights.
What are lighting pole arms and brackets and how are they selected
A Lighting pole arm bracket is the hardware that secures the light to the structure. Arm brackets are selected based on specific fixture mounting requirements. You must choose a bracket that fits the diameter of the arm and allows for the necessary degree of tilt. Selecting the right bracket is what ensures your light stays pointed at the road rather than shifting due to vibration or wind over time.
How should planners determine the correct street light pole height
Effective Street light pole height guide strategies revolve around coverage design. Planners use pole height planning to ensure the light from one pole overlaps correctly with the next. The higher the pole, the further apart they can be spaced, which saves on project costs. However, this must be balanced with the power of the lamp to ensure the light is still bright enough when it finally reaches the road surface.
How do aluminum and steel light poles compare in real applications
The Aluminum vs steel light poles debate often comes down to weight and rust. Aluminum poles are valued for their light weight and resistance to salt, making them perfect for coastal cities. Steel poles offer the high-tension strength needed for incredibly tall installations or high-wind areas. In real-world applications, planners choose steel for its raw power and aluminum for its low-maintenance longevity.
What does a tapered light pole design achieve structurally
The Tapered light pole explained focuses on load efficiency. A tapered design moves material to the base where stress is highest. This shape naturally dampens vibrations and resists the “pendulum effect” caused by wind hitting the light fixture. It is a highly efficient way to build a pole that is both strong and relatively light, making it the standard for modern roadway engineering.
How is wind load calculated for street light poles
A Light pole wind load calculation involves determining the wind pressure exerted on the surface of both the pole and the fixture. This structural calculation is vital to ensure the pole doesn’t buckle. Engineers look at the “EPA” (Effective Projected Area) of the light fixture to determine how much force will be transferred to the pole, ensuring the assembly is safe for the local wind zone.
When should single or double arm brackets be used
Single vs double arm bracket decisions are based on roadway layout. A single arm is perfect for standard roadside poles, while a double arm is preferred for median-mounted poles that need to light two directions at once. Using a double-arm bracket on a single median pole is a smart way to maximize the utility of the hardware while maintaining a clean look for the highway.
Why is a proper street light pole foundation essential for long-term stability
The Street light pole foundation provides the ultimate structural stability. Without a correctly engineered foundation design, the pole is susceptible to leaning. A solid concrete base ensures that the pole stays vertical and the light stays aimed correctly for decades. It is the most critical part of the installation because once it is poured, it is the hardest part to fix or replace.
Final Thought
When you treat street light poles, arms, and brackets as an integral part of your lighting design rather than an afterthought, you create a road environment that is safer, more durable, and cost-effective. The physical structure is what translates your lumen and wattage plans into actual visibility on the pavement. By prioritizing the right mounting geometry and structural stability, you ensure that your community benefits from clear, uniform light that stands the test of time.



- 10 Meters Lamp Post
- 10 Meters Pole
- 1000w Led Projector
- 100W LED Tunnel Light
- 12 Meters Lamp Post
- 12 Meters Pole
- 1200w Led Projector
- 15 Light Pole
- 1500w Led Projector
- 150W LED Tunnel Light
- 1800w Led Projector
- 2 In 1 Solar Flood Light
- 200w Led Tunnel Light
- 50w Led Tunnel Light
- 6 Meters Lamp Post
- 6 Meters Pole
- 8 Meters Lamp Post
- 8 Meters Pole
- 800w Led Projector
- 80w Led Tunnel Light
- Colourful Decorative Light
- Conical post
- Courtyard Lamp
- courtyard light
- courtyard lighting fixture
- Decorative Landscape Light
- Decorative road Light
- Flood Light For Courtyard
- Flood Light for Garden
- Flood Light For Outdoor
- Foot Led High Bay Lights
- high bay led lights 100w
- industrial lampshade
- industrial LED shed lights
- industrial magnifying glass with light
- Integrated Solar Flood Light
- led courtyard lamp
- led courtyard light
- led high bay light 100w
- LED Projector For Stadium
- Led UFO High Bay 150W 5000k
- Lighting Plants Mining Price
- Maintenance Free LED Street Light
- Pic Controlling Tunnel Light
- PLC controlling tunnel light
- Post Top Garden Light
- RGB Landscape Light
- Rgbw Decorative Light
- Smart Tunnel Light
- solar courtyard lamp
- solar courtyard light
- Solar LED Road Light
- Solar Street Light For 10 Meter Pole
- Solar Street Light For 12 Meter Pole
- Solar Street Light For 6 Meter Pole
- Solar Street Light For 8 Meter Pole
- Split Type Solar Flood Light
- Sporting Projector
- Stadium Led Projector
- Street Lighting Post
 FACEBOOK
FACEBOOK
 TWITTER
TWITTER
 LINKEDIN
LINKEDIN