Solar street lighting systems complete buying and specification guide
Solar street lighting systems rely on solar power as the core energy source, providing a decentralized and sustainable method to illuminate public spaces. As a robust street lighting infrastructure solution, these systems allow for rapid deployment in areas where traditional power grids are inaccessible or too costly to extend.
The decision logic for choosing solar over grid-based lighting typically centers on the reduction of trenching expenses and the need for independent, resilient energy. Buyers can select from several types of solar street lighting systems, ranging from integrated all-in-one units to high-output split configurations. System performance is dictated by solar panel sizing, which ensures that photovoltaic panels capture enough energy to meet the fixture’s demand.
Complementing this, battery capacity and battery storage define the nightly operation and the system’s ability to remain functional during multi-day outages. Professional engineering also accounts for cloudy and low-sun performance to guarantee reliability in varying climates.
Furthermore, specific wattage selection based on road width is required to meet safety and illumination standards. While initial prices vary, the primary cost drivers and lifecycle value often make solar more economical than grid-connected alternatives.
Before finalizing a project, approval evaluation criteria such as site shading and load requirements must be verified. This comprehensive assessment leads to a final suitability decision based on the specific operational goals of the installation site.
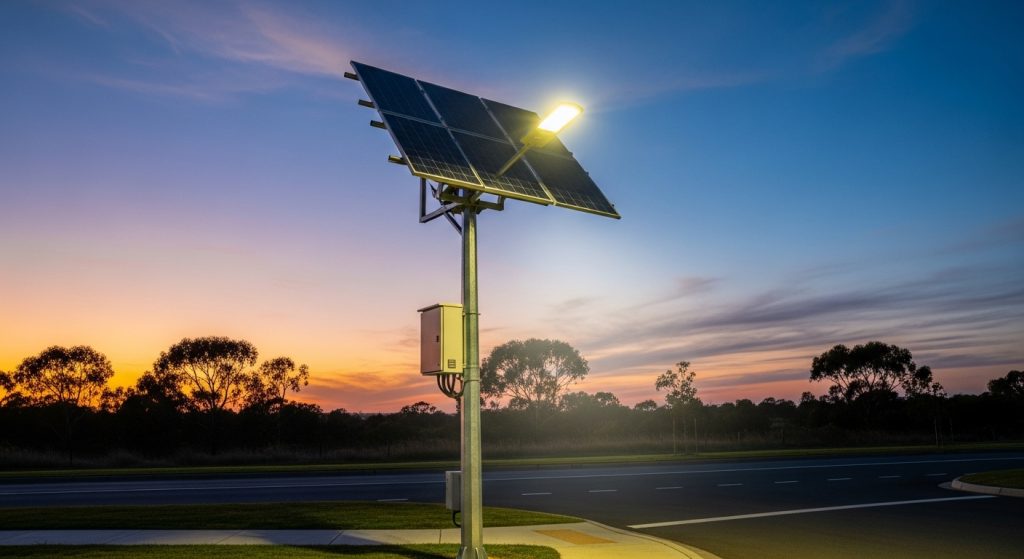

Why solar power is used for street lighting systems?
Utilizing solar power for outdoor lighting networks has become a standard practice in modern urban and rural development. The primary driver is the ability to establish off-grid infrastructure without the prohibitive costs associated with expanding the traditional electrical utility. Traditional lighting requires extensive trenching, cabling, and transformer upgrades, whereas solar units operate as autonomous energy plants. This independence translates into significant long-term electricity savings, as the system harvests renewable energy during daylight hours to power the illumination at night.
Furthermore, solar power is used to ensure high levels of resilience. In the event of a grid failure or natural disaster, these systems remain operational, maintaining public safety on roadways and in residential areas. The modular nature of solar lighting also allows for incremental deployment, meaning a project can be expanded as needed without redesigning a central power circuit. For municipalities and developers aiming to meet sustainability targets, solar energy offers a zero-emission solution that minimizes the environmental footprint of essential infrastructure while reducing the recurring costs associated with utility-based lighting services.
What is a solar street lighting system?
A solar street lighting system is an integrated illumination assembly that converts sunlight into electrical energy to provide nighttime light. The power flow begins with photovoltaic panels, which are typically mounted at the top of the pole to maximize exposure to solar radiation. These panels generate direct current (DC) electricity that is regulated by a charge controller. This controller is the “brain” of the system, managing the energy flow to prevent overcharging and to ensure that the battery storage unit is charged efficiently and safely.
The stored energy is held within the battery—usually a lithium-based chemistry—until the ambient light levels drop below a certain threshold. At dusk, the controller triggers the release of energy to the LED street lights. LEDs are utilized because of their high luminous efficacy, which provides maximum brightness with minimal energy consumption. This entire process is self-contained and automated, allowing the system to function as a reliable, off-grid light source that operates without external wiring or manual switching, providing a sustainable and low-maintenance lighting solution for varied environments.
When should buyers choose solar over grid-based street lighting?
Deciding between solar and grid-based lighting depends largely on the proximity of the project site to existing electrical infrastructure. When grid access is unavailable or requires a distance of more than a few hundred meters, the cost of extending utility lines can easily exceed the price of independent solar units. Buyers should prioritize solar when the financial burden of infrastructure expansion is high, particularly in remote areas or sites where the landscape prevents easy cabling.
Another major consideration is the avoidance of trenching costs. In developed urban areas, cutting through existing concrete, asphalt, or landscaping to lay wires is expensive and disruptive. Solar systems require no underground connections, making them much faster to install.
Buyers should select solar street lighting in the following scenarios:
- Off-Grid Locations: Sites where the cost of a new transformer or grid tie-in is commercially unviable.
- Fast-Track Projects: Developments that require lighting to be operational immediately without waiting for utility company approvals.
- Environmentally Sensitive Areas: Locations where digging trenches would damage protected habitats or tree root systems.
- High-Maintenance Grids: Regions with frequent power outages where lighting must remain active for public safety.

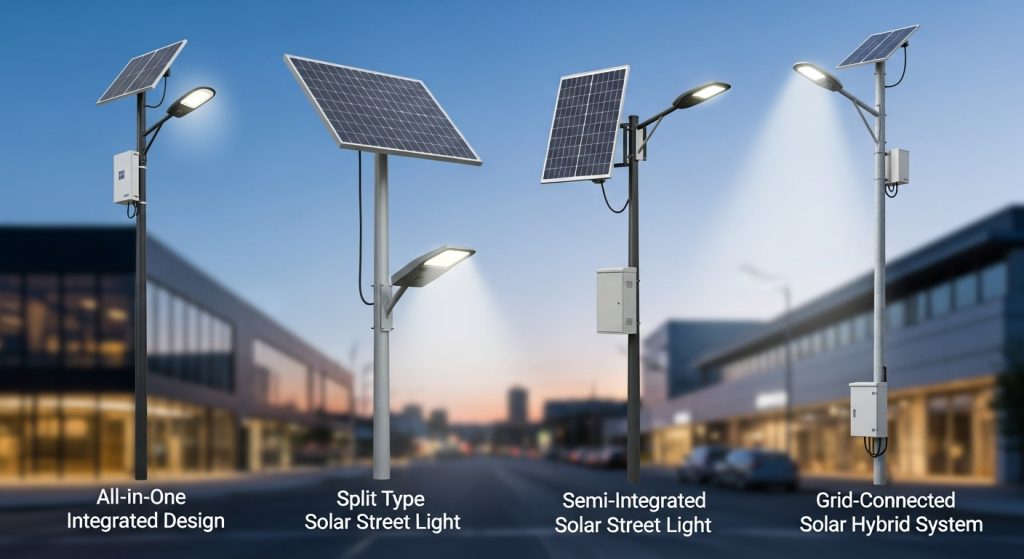
Which type of solar street lighting system should you buy?
The selection of a specific system architecture depends on the lighting requirements, mounting constraints, and local environmental conditions. Modern solar lights are built with a modular design, allowing buyers to choose a configuration that balances installation flexibility with power output. For instance, a small pedestrian pathway has different technical needs than a six-lane highway, and the chosen system type must reflect these differences to ensure long-term performance and reliability.
When evaluating your project needs, consider the following primary categories:
- All-in-one solar street lights: These systems integrate the panel, battery, and LED into a single housing. They are best for ease of installation and low-wattage applications like parks or residential streets.
- Split-type solar street lights: In this setup, the panel, battery, and light are separate. This is ideal for high-power requirements as it allows for much larger panels and batteries.
- Semi-integrated solar street lights: These offer a balance, usually combining the battery and light while keeping the solar panel separate for adjustable positioning.
- Grid-connected solar hybrid systems: These units use solar as the primary source but remain connected to the grid as a backup for extreme weather situations.

How solar panel size affects street light performance?
The size and efficiency of the photovoltaic panels are the primary factors in determining how much energy generation a system can achieve daily. To ensure the light stays on all night, the solar input must exceed the energy demand of the LED fixture. Professional specifications use an “oversizing logic,” where the panel is sized to produce more energy than the light strictly needs on a perfect sunny day. This creates a buffer to account for dust accumulation, atmospheric haze, and the lower efficiency of panels over time.
Seasonal variation is the most critical challenge for panel sizing. During winter months, solar irradiation is lower and daylight hours are shorter, yet the lighting demand is higher due to longer nights. If the photovoltaic output is insufficient, the battery will never reach a full state of charge, leading to system failure. Therefore, matching the panel wattage to the geographical location’s “worst month” solar data is essential. A correctly sized panel ensures that the system generates enough power even during the most difficult times of the year, maintaining consistent illumination.
How battery capacity determines nightly lighting duration?
The energy storage capacity of the system serves as the reservoir that fuels the LED fixture through the night. In modern systems, the lithium battery is the preferred technology because it can handle many discharge cycles without significant battery degradation. The capacity must be large enough to cover the total watt-hours required for the intended lighting schedule, while also providing “autonomy days”—the ability to run the light for multiple nights even if there is zero sun the following day.
The depth of discharge (DoD) is also a vital specification. If a battery is regularly drained to 0%, its lifespan will drop drastically. High-quality specifications usually limit the nightly draw to 20–30% of the total capacity, ensuring the battery stays within a healthy operating range. If the capacity is too small for the wattage of the light, the system will shut down prematurely, or the battery will fail within a year or two. A well-sized battery ensures that the light maintains its full brightness from dusk to dawn, regardless of the previous day’s weather conditions.
How solar street lights perform in cloudy or low-sun conditions?
Ensuring performance reliability during periods of cloudy weather is a cornerstone of professional solar lighting design. While it is true that reduced solar input occurs during overcast days, high-quality panels are still capable of generating power from diffused sunlight. Climate-based planning involves analyzing historical weather data for the installation site to determine how many consecutive cloudy days the system must endure. This is where the synergy between the panel and the battery becomes critical.
To manage performance in low-sun regions, smart controllers use battery buffering and adaptive dimming. If the controller detects that the battery voltage is dropping below a safe threshold due to lack of sun, it may automatically reduce the brightness of the LEDs to conserve power. This ensures the light stays on—albeit at a lower intensity—rather than failing completely. By specifying systems with higher-efficiency monocrystalline panels and larger storage reserves, buyers can guarantee that their outdoor lighting remains functional even in environments that do not receive constant, direct sunlight.
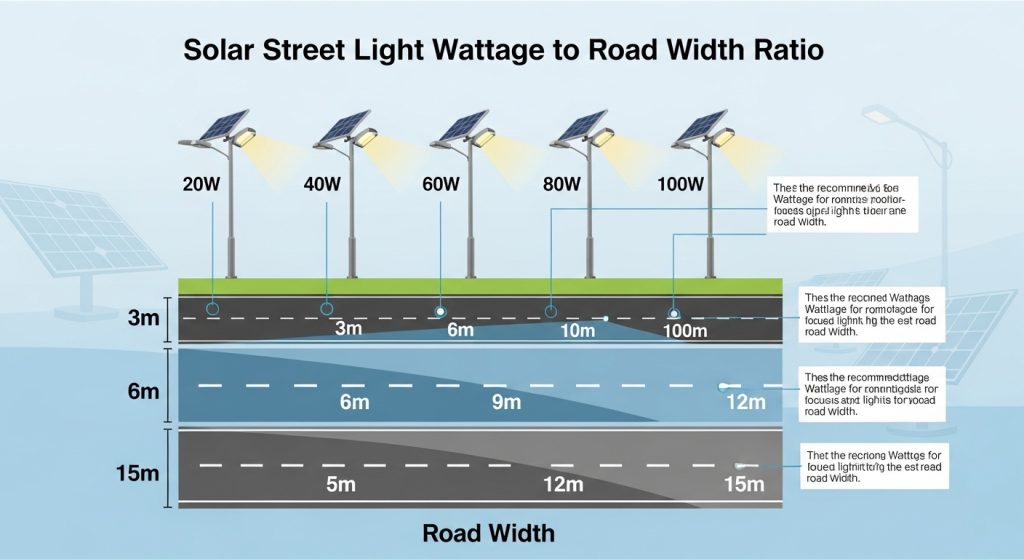
How to match solar street light wattage to road width?
Choosing the correct LED wattage is essential for maintaining road safety and achieving proper illumination levels. If the wattage is too low for the road width, the light will not reach the edges of the pavement, creating dark spots that are hazardous for drivers and pedestrians. Conversely, if the wattage is too high, it leads to excessive glare and wasted energy. The specification must consider the road classification and the required uniformity of the light distribution.
To ensure the system meets local safety standards, follow these general matching guidelines:
- Narrow Pathways (3–5 meters): Typically require 15W to 30W LEDs to provide adequate security and visibility for pedestrians.
- Residential/Local Roads (6–8 meters): Usually necessitate 40W to 60W fixtures to ensure safe vehicle passage and sidewalk coverage.
- Collector/Secondary Roads (8–10 meters): Often demand 80W to 100W systems, usually requiring higher mounting heights for better spread.
- Major Arterial Roads (12+ meters): Require 120W+ high-output LEDs, often using specialized optics to project light across multiple lanes.
What determines the real cost of solar street lighting systems?
The lifecycle cost of a solar street lighting system is influenced by more than just the initial purchase price. While the capital investment for a solar unit is often higher than a standard grid fixture, the elimination of monthly utility bills and expensive underground infrastructure provides a rapid return on investment. The primary cost driver is component quality; for example, high-grade LiFePO4 batteries and efficient solar cells cost more upfront but last twice as long as cheaper alternatives.
Another factor is maintenance planning. Because solar lights are independent units, there are no underground wiring faults to repair, which is often the most expensive part of maintaining grid-based systems. However, the cost of the pole, the foundation, and the labor for installation must be factored into the total budget. Buyers should evaluate the total cost of ownership over a 10-year period, as high-quality solar systems typically become the more economical choice by year three or four when compared to the combined energy and maintenance costs of a traditional lighting network.
What buyers should evaluate before approving a solar street lighting project?
Approving a solar lighting project requires a thorough project feasibility assessment to ensure the system will meet its operational requirements. The most important step is a site survey to check for solar exposure. If a pole is placed under a tree canopy or in the shadow of a tall building, the system will likely fail regardless of how high its specifications are. Buyers must verify that the installation site receives enough unshaded sun hours during the winter to charge the batteries.
The evaluation process should include the following:
- Solar Resource Analysis: Use geographic data to confirm the average peak sun hours for the location.
- Load Assessment: Determine the total energy consumption of the LED based on the desired lighting schedule (e.g., 100% brightness for 4 hours, then 30% for the rest of the night).
- Operational Planning: Confirm that the chosen system architecture (all-in-one vs. split) is appropriate for the local wind speed and mounting requirements.
- Warranty and Support: Ensure the manufacturer provides long-term warranties on the battery and controller, which are the most critical components.
Is a solar street lighting system the right choice for your project?
A final determination on project suitability involves comparing the operational requirements of the site with the inherent strengths of solar technology. Solar lighting is the ideal choice for new construction, remote areas, and projects where sustainability is a priority. It is particularly effective for parking lots, parks, and secondary roads where the cost of trenching for grid power would be disproportionately high. The neutral guidance for buyers is to look at solar as a long-term infrastructure investment that provides energy independence and safety.
However, solar may not be the right choice for high-density urban areas with significant “sky-view” obstructions or for locations in extreme northern latitudes with months of near-total darkness. In these cases, a grid-connected or hybrid system is often more practical. For the majority of outdoor applications, a well-engineered solar street lighting system offers the best balance of performance, cost-efficiency, and environmental responsibility, provided that the technical specifications are correctly matched to the local environment.
What is an all-in-one solar street light system?
An all-in-one solar street light utilizes an integrated design where the solar panel, battery, and LED source are all contained within a single compact housing. This setup is highly valued for its compact solar lighting footprint and ease of transport. Because all components are pre-wired, the installation process is as simple as mounting the unit onto a pole and turning it on. These systems are most commonly used for residential streets, perimeter security, and parks. To learn more about selecting these integrated units, see our all-in-one solar street light guide.
When is a split-type solar street light the better option?
A split type solar street light is the preferred choice for high-power lighting applications. By using a modular configuration, the solar panel can be sized much larger than the light fixture itself, which is necessary for 100W+ LED outputs. This design also allows the panel to be angled independently toward the sun, maximizing energy harvest in locations with limited direct light. It is the standard solution for highways and large industrial facilities that require high illumination levels throughout the night without compromise.
What is a semi-integrated solar street light design?
The semi integrated solar street light offers a hybrid structure that combines the simplicity of integrated lights with the performance of split systems. Usually, the battery and LED are integrated into the light head, while the solar panel remains a separate, adjustable piece. This provides flexible installation options, allowing installers to point the light toward the road while tilting the panel for optimal solar gain. It is an excellent middle ground for projects that need more power than an all-in-one unit but want to avoid the complexity of a full split-type setup.
When should grid-connected solar hybrid lighting be used?
In areas where energy reliability is a non-negotiable requirement, grid connected solar hybrid lighting should be used. These systems prioritize solar energy but feature a grid backup that automatically takes over if the battery storage is depleted by a long series of cloudy days. This is common in high-traffic urban intersections or critical military and medical facilities. It offers the financial benefits of solar energy savings while providing the absolute security of a traditional grid connection during extreme environmental conditions.
How long do solar street light batteries last?
Understanding the solar street light battery lifespan is essential for long-term maintenance planning. Most modern lithium-ion or LiFePO4 batteries are designed to last between 5 and 10 years, depending on their charge cycles and local temperatures. High heat is a major factor in battery degradation, so units installed in desert climates may require replacement sooner than those in temperate zones. Regularly monitoring the battery’s performance and ensuring it is never fully depleted will help maximize the service life of the energy storage system.
How do solar street lights work during cloudy weather?
Performance during solar street lights cloudy weather is achieved through a combination of high-efficiency solar cells and system resilience strategies. Even when the sky is overcast, panels can still generate a significant portion of their rated power. The system relies on its battery buffer—the extra energy stored during sunny days—to maintain light output. Many smart controllers also implement power-saving modes during low-sun periods to ensure that the light continues to function, albeit at a slightly dimmed level, until the batteries can be fully recharged.
How to size solar panels for street lighting projects?
To correctly size solar panels street lighting, engineers must calculate the total daily energy consumption of the LED fixture and compare it to the available solar exposure at the site. The panel wattage must be high enough to fully recharge the battery even during the shortest days of winter. Factors such as the angle of the panel and local dust levels should be included in the calculation. A properly sized panel prevents the battery from entering a deep discharge state, which is the most common cause of premature system failure in solar lighting projects.
What affects solar street light cost per pole?
Several cost drivers impact the final budget of a project, including the project scale and the specific technology chosen. High-lumen LEDs and high-capacity lithium batteries carry a premium price but offer a lower total cost of ownership over time. The material and height of the pole, along with the complexity of the foundation needed for local wind conditions, also contribute significantly to the total cost per pole. Buyers should seek a balance between initial capital expenditure and the long-term reliability of the internal electronic components.
How to choose solar street light wattage for road width?
When you choose solar street light wattage road width, the goal is to meet international illumination standards while maximizing energy efficiency. Wider roads require high-wattage LEDs paired with specialized lenses that project light horizontally across multiple lanes. On narrower residential streets, a lower wattage is sufficient to provide safe roadway coverage without creating light pollution in neighboring homes. Correctly matching the wattage ensures that the project provides the best possible visibility for its specific geometric layout.
Final Thought
Successfully implementing a solar street lighting project requires more than just purchasing hardware; it necessitates a detailed understanding of the synergy between energy harvesting, storage, and distribution. By focusing on site-specific sizing and component quality, project managers can ensure that their lighting infrastructure provides reliable, cost-effective service for a decade or more. As technology continues to advance, the gap between solar and traditional lighting will only widen, making solar the definitive standard for sustainable outdoor illumination.



- 10 Meters Lamp Post
- 10 Meters Pole
- 1000w Led Projector
- 100W LED Tunnel Light
- 12 Meters Lamp Post
- 12 Meters Pole
- 1200w Led Projector
- 15 Light Pole
- 1500w Led Projector
- 150W LED Tunnel Light
- 1800w Led Projector
- 2 In 1 Solar Flood Light
- 200w Led Tunnel Light
- 50w Led Tunnel Light
- 6 Meters Lamp Post
- 6 Meters Pole
- 8 Meters Lamp Post
- 8 Meters Pole
- 800w Led Projector
- 80w Led Tunnel Light
- Colourful Decorative Light
- Conical post
- Courtyard Lamp
- courtyard light
- courtyard lighting fixture
- Decorative Landscape Light
- Decorative road Light
- Flood Light For Courtyard
- Flood Light for Garden
- Flood Light For Outdoor
- Foot Led High Bay Lights
- high bay led lights 100w
- industrial lampshade
- industrial LED shed lights
- industrial magnifying glass with light
- Integrated Solar Flood Light
- led courtyard lamp
- led courtyard light
- led high bay light 100w
- LED Projector For Stadium
- Led UFO High Bay 150W 5000k
- Lighting Plants Mining Price
- Maintenance Free LED Street Light
- Pic Controlling Tunnel Light
- PLC controlling tunnel light
- Post Top Garden Light
- RGB Landscape Light
- Rgbw Decorative Light
- Smart Tunnel Light
- solar courtyard lamp
- solar courtyard light
- Solar LED Road Light
- Solar Street Light For 10 Meter Pole
- Solar Street Light For 12 Meter Pole
- Solar Street Light For 6 Meter Pole
- Solar Street Light For 8 Meter Pole
- Split Type Solar Flood Light
- Sporting Projector
- Stadium Led Projector
- Street Lighting Post
 FACEBOOK
FACEBOOK
 TWITTER
TWITTER
 LINKEDIN
LINKEDIN